So, you’re facing another brutal winter, and you’ve finally decided that it’s time to invest in a snowblower. Makes sense, considering the back-breaking work of shoveling snow, right? But before you go out and make a purchase, you need to understand the key differences between residential and industrial snowblowers. It’s not just about the price tag or the size; there’s a lot more to consider. In this article, we’ll break down the main distinctions between these two types of snowblowers, giving you the information you need to make an informed decision and ensure a snow-free driveway or parking lot.

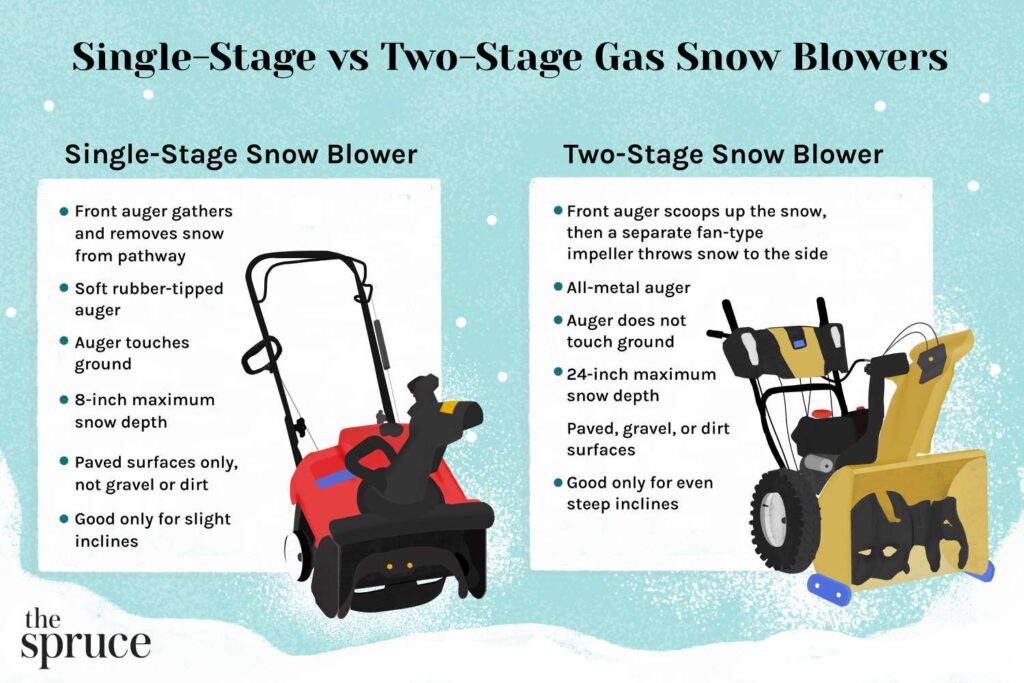
Capacity and Power
Residential snowblower power
Residential snowblowers are typically designed for smaller areas and lighter snowfalls. They are equipped with smaller engines, ranging from around 5 to 15 horsepower. These machines have enough power to effectively clear driveways, walkways, and small to medium-sized yards. The power of residential snowblowers is sufficient for most homeowners’ needs.
Industrial snowblower power
On the other hand, industrial snowblowers are built to handle heavy-duty snow clearing tasks. They are equipped with much larger and more powerful engines, usually ranging from 20 to 40 horsepower or more. This increased power allows industrial snowblowers to tackle larger areas, such as parking lots, roads, and commercial properties. The higher horsepower of industrial snowblowers enables them to throw snow farther and clear larger amounts of snow in a shorter time.
Residential snowblower capacity
Residential snowblowers typically have smaller capacities compared to their industrial counterparts. They are designed to handle lighter snowfalls and have smaller snow intake chutes and impellers. The capacity of residential snowblowers usually ranges from around 500 to 1500 pounds per minute. This capacity is sufficient for residential use and can effectively clear moderate amounts of snow in a timely manner.
Industrial snowblower capacity
Industrial snowblowers, being designed for heavy-duty use, have much larger capacities to handle large amounts of snow. They have wider snow intake chutes and more powerful impellers, allowing them to handle snow at a faster rate. The capacity of industrial snowblowers can range from 1500 to 4000 pounds or more per minute, depending on the model. This high capacity is necessary for quickly clearing large areas and efficiently managing heavy snowfalls.
Design and Construction
Residential snowblower design
Residential snowblowers are generally designed to be compact and maneuverable. They are often smaller in size and lighter in weight compared to industrial snowblowers. The design of residential snowblowers focuses on ease of use and storage, with features such as foldable handles and compact storage options. The design also emphasizes user safety, with controls and safety features that are generally more user-friendly.
Industrial snowblower design
Industrial snowblowers are typically larger and heavier than residential models. They are designed to withstand the demands of heavy-duty use in extreme weather conditions. The design of industrial snowblowers prioritizes functionality and durability. These machines are built with robust frames, heavy-duty components, and reinforced structures to handle the rigors of continuous operation in harsh winter conditions. Industrial snowblowers also often have features like adjustable skid shoes and heated handles for enhanced performance and comfort.
Residential snowblower construction
The construction of residential snowblowers is focused on affordability without compromising quality. The frames of residential models are typically made from lightweight materials such as aluminum, which makes them easier to handle and transport. The components used in residential snowblowers are durable enough for regular residential use but may not withstand the demands of continuous heavy-duty usage.
Industrial snowblower construction
Industrial snowblowers are constructed with heavy-duty materials to ensure longevity and durability. The frames of industrial models are usually made from sturdy steel or reinforced metal alloys, providing robustness and protection against the challenges of heavy snow and regular use. The components used in industrial snowblowers are designed to withstand the demands of continuous operation in harsh weather conditions. Industrial models often incorporate high-quality bearings, reinforced belts, and heavy-duty drivetrains to ensure reliable performance.
Snow Throwing Distance
Residential snowblower throwing distance
Residential snowblowers have a limited snow throwing distance compared to their industrial counterparts. On average, residential snowblowers can throw snow up to around 20 to 30 feet. This range is sufficient for clearing driveways, walkways, and small to medium-sized yards. However, a shorter throwing distance means that the cleared snow needs to be deposited closer to the designated area, requiring some extra manual effort for further disposal if needed.
Industrial snowblower throwing distance
Industrial snowblowers have a much greater snow throwing distance to effectively clear large areas. These machines are capable of throwing snow anywhere from 40 to 60 feet or more, depending on the model. The longer throwing distance allows industrial snowblowers to clear snow from large parking lots, roadways, and commercial properties without needing to repeatedly cover the same area. The extended throwing distance also enables efficient snow disposal and reduces the need for manual labor.
Clearing Path Width
Residential snowblower clearing path width
Residential snowblowers typically have narrower clearing paths compared to industrial models. The clearing path width of residential snowblowers ranges from around 18 to 30 inches. These widths are suitable for most residential driveways and walkways, allowing homeowners to clear snow efficiently. Due to the narrower clearing path, however, it may take slightly longer to clear larger areas using a residential snowblower.
Industrial snowblower clearing path width
Industrial snowblowers boast wider clearing paths to cover larger areas in a shorter time. The clearing path width of industrial models can range from 30 to 50 inches or more. This broader path width allows industrial snowblowers to quickly and efficiently clear wide parking lots, expansive roads, and large commercial properties. The wider clearing path significantly reduces the time required for snow removal, increasing productivity for commercial snow-clearing operations.
Price Range
Residential snowblower price range
Residential snowblowers are generally more affordable compared to industrial models. The price range for residential snowblowers varies depending on the brand, model, and features included. On average, residential snowblowers can be purchased for as low as $300, with higher-end models reaching up to $1500. The affordability of residential snowblowers makes them a practical choice for homeowners looking for efficient and cost-effective snow removal solutions.
Industrial snowblower price range
Industrial snowblowers come at a higher price point due to their larger size, increased power, and heavy-duty construction. The price range for industrial snowblowers can vary significantly, depending on the brand, model, and additional features. Generally, industrial snowblowers start from around $2000 and can go up to $10,000 or more for top-of-the-line models. The higher price tag is justified by the capabilities and durability of industrial snowblowers, which are designed for professional and commercial use.
Durability and Lifespan
Residential snowblower durability
Residential snowblowers are designed to withstand regular residential use and occasional heavy snowfall. While they are built to be durable, the components and materials used in residential models are not as heavy-duty as those found in industrial snowblowers. With proper maintenance and care, a well-built residential snowblower can last for several years. However, if continuously subjected to heavy-duty tasks or not adequately maintained, the overall durability and lifespan of residential snowblowers may be compromised.
Industrial snowblower durability
Industrial snowblowers are built to withstand heavy-duty use in extreme winter conditions. They are specifically engineered and constructed to handle demanding snow-clearing tasks for extended periods. The robust construction and high-quality components of industrial models result in superior durability and longevity. With proper maintenance, an industrial snowblower can last for many years or even decades, providing reliable performance in commercial or professional snow removal operations.
Residential snowblower lifespan
The lifespan of a residential snowblower can vary depending on various factors such as the brand, model, usage frequency, and maintenance. On average, a well-maintained and properly used residential snowblower can last between five to ten years. Regular maintenance, including oil changes, lubrication, and proper storage during the offseason, can significantly extend the lifespan of a residential snowblower.
Industrial snowblower lifespan
Industrial snowblowers are built to endure the toughest winter conditions and heavy usage. With regular maintenance and proper care, an industrial snowblower can last for fifteen years or more. The exceptional durability and longevity of industrial models make them a worthwhile investment for businesses and professionals who require reliable and efficient snow removal equipment.
Operating Noise
Residential snowblower noise level
Residential snowblowers are designed to minimize noise levels to ensure a quieter operation. While the noise level can vary depending on the specific model, residential snowblowers typically produce noise levels ranging from 70 to 90 decibels (dB). While not completely silent, the noise level of residential snowblowers is generally tolerable and is unlikely to cause significant disturbance to neighbors or individuals nearby.
Industrial snowblower noise level
Industrial snowblowers typically produce higher noise levels compared to their residential counterparts due to their larger engines and more powerful performance. The noise level of industrial snowblowers can range from 80 to 100 decibels (dB) or higher, depending on the model and specific operating conditions. The increased noise level is a trade-off for the enhanced power and snow-clearing capabilities offered by industrial snowblowers. However, it is important to note that ear protection is recommended when operating any snowblower, regardless of the noise level.
Ease of Use
Residential snowblower ease of use
Residential snowblowers are designed with user-friendliness in mind. They are generally lighter in weight, have more compact dimensions, and feature intuitive controls. The compact size and maneuverability of residential snowblowers make them easy to handle and navigate, especially in tighter residential areas. Start-up procedures for residential snowblowers are typically straightforward, and many models include additional features such as electric start or single-button push start for added convenience.
Industrial snowblower ease of use
Industrial snowblowers may require more familiarity and experience to operate effectively due to their larger size and increased power. While they may initially feel more challenging to handle, industrial snowblowers are designed with advanced controls and features that improve ease of use. Many industrial models include features like power steering, adjustable chute controls, and joystick controls for precise operation. With proper training and practice, operators can become accustomed to the operation of industrial snowblowers and achieve efficient snow-clearing results.
Portability
Residential snowblower portability
Residential snowblowers are designed to be relatively portable for easy maneuverability and storage. Their compact size and lighter weight allow homeowners to transport them in the trunk of a car or store them in a smaller shed or garage. Many residential snowblowers also feature foldable handles and wheels for convenient transportation and storage. The portability of residential snowblowers ensures that homeowners can easily move them around their property and store them when not in use.
Industrial snowblower portability
Due to their larger size and heavier weight, industrial snowblowers are less portable compared to residential models. These machines often require trailers or trucks for transportation and may have specific storage requirements. Industrial snowblowers are commonly used in fixed or semi-permanent locations where they can be easily accessed for snow removal purposes. Despite their reduced portability, industrial snowblowers are designed to be moved and deployed efficiently in the areas they are intended to clear.
Maintenance Requirements
Residential snowblower maintenance requirements
Residential snowblowers typically have simpler maintenance requirements compared to industrial models. Regular maintenance tasks for residential snowblowers include oil changes, air filter cleaning or replacement, lubrication of moving parts, and general inspection of belts and cables. These maintenance tasks can usually be done by the owner with basic tools and knowledge, ensuring the snowblower’s continued performance and reliability.
Industrial snowblower maintenance requirements
Industrial snowblowers require more extensive and regular maintenance due to their heavy-duty use. Maintenance tasks for industrial snowblowers may include more frequent oil changes, inspections of belts, bearings, and drivetrain components, as well as periodic greasing of pivot points. Some industrial models may also require specialized maintenance procedures, including engine tune-ups, hydraulic system checks, and more. Given the complexity and demands of industrial snowblowers, it is often recommended to have a trained technician or service professional perform the maintenance to ensure proper and thorough servicing.
In conclusion, residential and industrial snowblowers differ significantly in terms of their power, capacity, design, construction, throwing distance, clearing path width, price range, durability, noise level, ease of use, portability, and maintenance requirements. Understanding these differences is essential for individuals or businesses choosing the right snowblower for their needs. By selecting the appropriate type of snowblower, you can efficiently and effectively clear snow, ensuring safety and convenience during the winter months.